IVD Kit Development: Integrating Silica Magnetic Beads into Diagnostic Workflows
SEO Keywords: IVD assay development, silica magnetic beads, nucleic acid purification kits, clinical diagnostics, automated workflow integration, reagent manufacturing.
The Strategic Importance of Raw Material Selection in IVD
For Diagnostic kit manufacturers, the "Research and Development" phase is only the beginning. Moving a molecular assay from the benchtop to a commercially viable In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) product requires a deep understanding of component stability and scalability. Among all components, silica magnetic beads are arguably the most critical for ensuring the purity of the input sample. This article examines the technical and strategic considerations for integrating these beads into a standardized diagnostic workflow.
Consistency: The North Star of Diagnostic Manufacturing
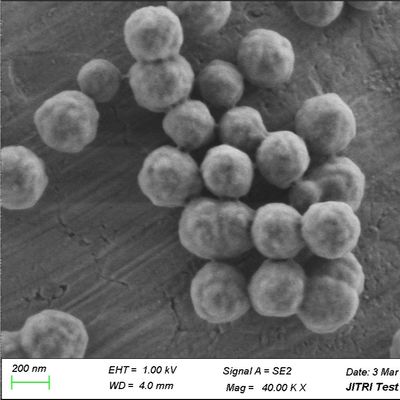
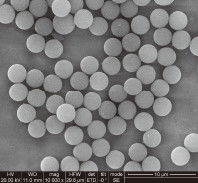
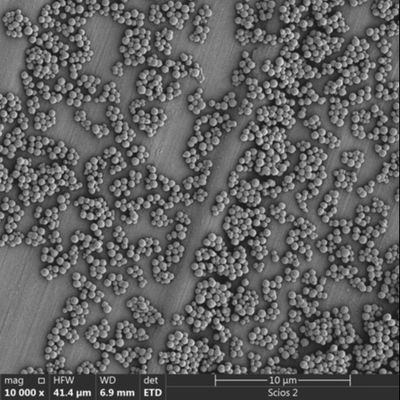
When an IVD company scales production to millions of tests per year, "variability" becomes the enemy. A slight change in the surface area or magnetic response of the beads can lead to inconsistent Limit of Detection (LoD) values.
-
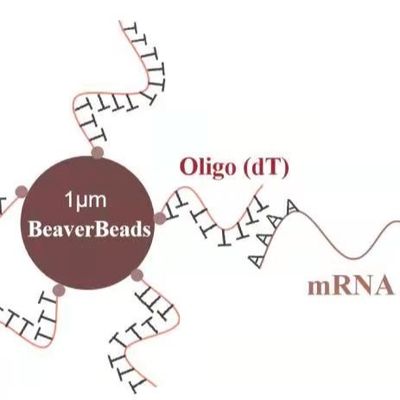
Surface Charge Density: Engineers must ensure that the silanol group density on the bead surface remains constant across different lots. This directly impacts the binding efficiency of DNA/RNA.
-
Superparamagnetism and Resuspension: In high-throughput clinical settings, beads must stay in suspension during the binding phase but aggregate instantly when the magnet is applied. Any "clumping" or residual magnetism can lead to bead carryover, which inhibits downstream qPCR or NGS enzymes.
Bridging the Gap Between Manual and Automated Workflows
Most IVD assays are designed to be "automation-ready." This means the silica magnetic beads must be compatible with liquid handling platforms (such as Hamilton, Tecan, or KingFisher).
-
Pipettability: Beads must be of a size (typically 1–3 $mu m$) that doesn't clog narrow pipette tips.
-
Standardization of Protocols: A well-engineered silica bead allows for a universal protocol—lysis, binding, washing, and elution—that can be programmed into any open-system robotic workstation.
-
Dead Volume Optimization: For high-cost reagents, minimizing the volume of beads required per reaction is essential for maintaining a competitive price-per-test.
Regulatory and Quality Assurance Requirements
For procurement and quality control (QC) teams, sourcing silica magnetic beads is a matter of compliance.
-
ISO 13485 Standards: Suppliers must demonstrate a quality management system that aligns with medical device manufacturing.
-
Traceability: Every batch of beads must be traceable back to its raw components ($Fe_3O_4$ and silica precursors).
-
Shelf-life Stability: Accelerated aging studies are required to prove that the beads remain functional for 12–24 months when stored in various buffer conditions.
The Economics of In-House vs. Outsourced Beads
Decision-makers often weigh the pros and cons of "buying vs. making." While large diagnostic conglomerates might attempt to synthesize their own beads, most mid-sized IVD players find that outsourcing to a specialized manufacturer reduces risk. Outsourcing provides access to proprietary coating technologies that prevent the leaching of iron ions, which are notorious PCR inhibitors.
Conclusion: Future-Proofing the Assay
As the industry moves toward 2026 and beyond, the focus is shifting to faster "sample-to-result" times. High-performance silica magnetic beads are the key to reducing the time-consuming purification step, allowing diagnostic companies to offer faster, more reliable kits to the clinical market.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!