H1: Silica Magnetic Beads – Advanced Solutions for Biomolecule Separation
Silica Magnetic Beads are critical components in modern separation science, offering high‑efficiency capture and purification of nucleic acids, proteins, and cells. With superior surface chemistry and magnetic responsiveness, these beads serve as indispensable tools in biotechnology, diagnostics, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and life science research. This article explores the fundamentals, advantages, and industrial applications of silica magnetic beads, providing actionable insights for procurement teams, engineers, and technical decision‑makers.
H2: What Are Silica Magnetic Beads? Core Features and Technology
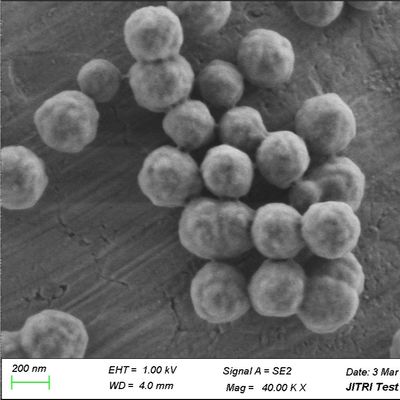
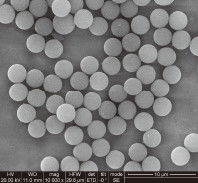
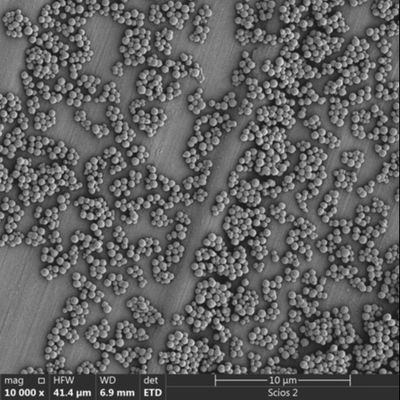
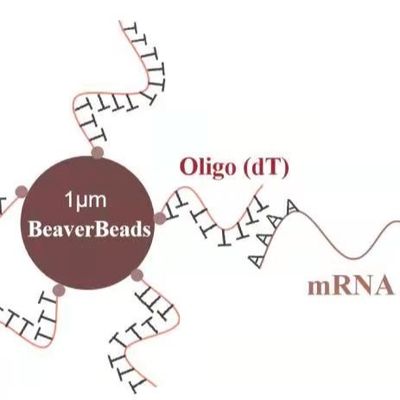
Silica Magnetic Beads consist of a magnetic core coated with silica (SiO₂), enabling strong magnetic response while providing a high‑affinity surface for binding biomolecules. The silica surface offers:
-
High surface area for efficient adsorption
-
Chemical stability across wide pH range
-
Compatibility with downstream processes
In contrast to uncoated magnetic particles, silica beads deliver greater reliability in DNA/RNA purification, immunoassays, and sample cleanup. Their uniform size distribution and surface quality ensure reproducible performance.
H3: How Magnetic Separation Works
Magnetic separation utilizes an external magnet to attract and immobilize magnetic beads bound to target molecules. The general workflow includes:
-
Binding: Silica magnetic beads are mixed with sample and binding buffer
-
Separation: A magnetic field is applied, pulling beads to vessel side
-
Washing: Impurities are washed away while beads remain trapped
-
Elution: Target biomolecules are released from bead surface
This procedure supports high throughput processing, minimal sample loss, and automation compatibility for industrial labs.
H2: Key Applications of Silica Magnetic Beads
H3: Nucleic Acid Purification and Genomic Workflows
One of the most important uses of silica magnetic beads is nucleic acid isolation for PCR, sequencing, and molecular diagnostics. Their high binding capacity and low inhibition profile enable:
-
Rapid extraction of DNA/RNA from blood, tissue, or environmental samples
-
Automated workflows for high throughput sequencing
-
Reliable performance in qPCR and NGS pipelines
Procurement teams seeking robust solutions should prioritize beads with consistent surface chemistry and validated performance data.
H3: Protein and Peptide Separation
Silica beads also contribute to protein purification workflows, especially when combined with affinity ligands. Their inert surface and controlled porosity make them suitable for proteomics applications.
H3: Cell Isolation and Immunoassays
In immunology and cell biology, silica magnetic beads facilitate:
-
Targeted capture of cells using antibody conjugation
-
Enrichment of rare cell populations
-
Automation of immunoassays for clinical diagnostics
H2: Choosing the Right Silica Magnetic Beads – Technical Considerations
Selecting the right magnetic beads requires evaluation of:
-
Particle size & uniformity: Smaller beads offer greater surface area but may affect separation speed
-
Surface chemistry & functionalization
-
Magnetic response strength
-
Compatibility with automation and buffer systems
For OEM applications, customization of surface coatings and bead sizes can greatly enhance process efficiency.
H3: Quality and Performance Metrics
Trusted suppliers provide:
-
Batch‑to‑batch consistency
-
Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
-
Technical support for assay integration
These elements are essential for clinical or regulated environments.
H2: Integration with Automation and High Throughput Systems
Industrial labs increasingly adopt automated platforms for nucleic acid extraction. Silica magnetic beads optimized for such systems deliver:
Thus, procurement leaders should assess vendor support for robotic compatibility and throughput scalability.
H2: Cost, Supply Chain, and Purchasing Strategy
When budgeting for silica magnetic beads, consider:
-
Per‑sample cost vs performance
-
Bulk procurement discounts
-
Vendor reliability and lead time
-
After‑sales technical support
A strategic purchasing plan ensures uninterrupted operations and cost optimization.
H2: Conclusion – Why Silica Magnetic Beads Matter
In today’s competitive biotech landscape, silica magnetic beads provide robust solutions for separation science across research and industrial workflows. Their versatility, reliability, and compatibility with automation make them a preferred choice for engineers, lab managers, and decision‑makers. Investing in high‑quality silica magnetic beads translates into reproducible results, scalable workflows, and operational efficiency.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!