The Strategic Guide to Silica Magnetic Beads for B2B Procurement and IVD Applications
SEO Keywords: Silica magnetic beads, nucleic acid extraction, magnetic particle manufacturing, IVD reagent components, automated DNA purification, B2B biotech procurement.
Introduction: The Backbone of Modern Molecular Diagnostics
In the rapidly evolving landscape of In Vitro Diagnostics (IVD) and biotechnology, the efficiency of nucleic acid isolation remains the most critical bottleneck. For procurement officers and lab directors, the choice of raw materials is not merely a technical decision but a strategic one. Silica magnetic beads have emerged as the gold standard for high-throughput, automated DNA and RNA purification. This article explores why these micro-scale particles are the cornerstone of the billion-dollar diagnostic industry and what decision-makers must consider when selecting a supplier.
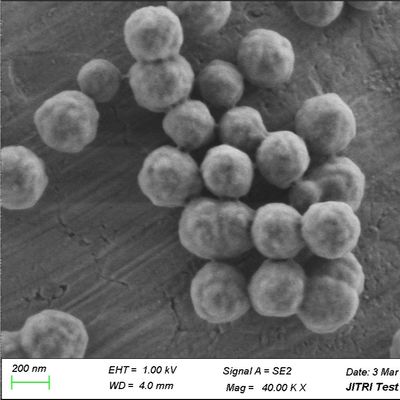
What are Silica Magnetic Beads?
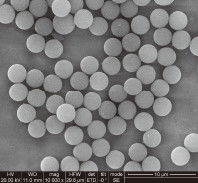
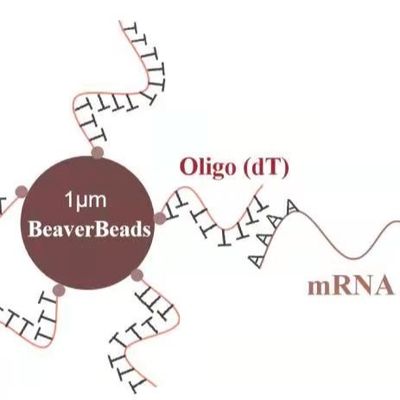
Silica magnetic beads are composite materials consisting of a superparamagnetic core (usually iron oxide) encapsulated in a high-purity silica shell. This core-shell structure combines the rapid separation capabilities of magnetism with the well-documented binding affinity of silica for nucleic acids under chaotropic conditions.
Why Decision-Makers Choose Silica Surface Chemistry
For engineers and B2B clients, the "Silica" part of the bead is vital. Unlike functionalized beads (like Carboxyl or Amine), silica beads utilize the "Charge Switch" or "Chaotropic Effect." In the presence of high concentrations of chaotropic salts (such as Guanidine HCl), the hydration shell of the DNA is disrupted, allowing it to bind specifically to the silica surface.
-
Scalability: The process is easily transitioned from a 24-well plate to 96-well or 384-well formats.
-
Consistency: High-purity silica provides a uniform surface area, ensuring that every batch of IVD kits performs identically.
-
Chemical Stability: Silica is inert to most biological buffers, ensuring a long shelf-life for diagnostic kits.
Key Technical Metrics for Engineering Teams
When evaluating a magnetic bead for industrial-scale use, engineers must look beyond the price per gram. The following metrics determine the total cost of ownership:
-
Saturation Magnetization: Usually measured in emu/g. Higher magnetization allows for faster separation in automated systems like the KingFisher™ or Bio-Rad platforms.
-
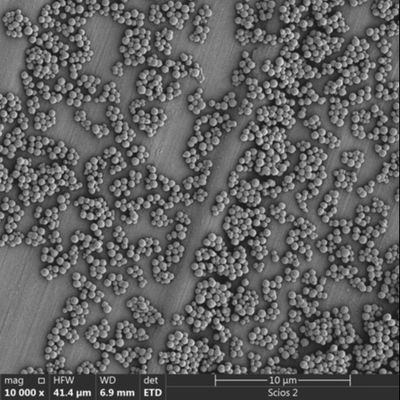
Particle Size Distribution (PSD): A narrow PSD ensures that beads don't settle too quickly in the reagent bottle, maintaining homogeneity during automated pipetting.
-
Binding Capacity: Measured in $mu g$ of DNA per mg of beads. High binding capacity means smaller reagent volumes and more compact kit designs.
Procurement Considerations: Choosing a Long-Term Partner
For procurement professionals, the focus shifts to supply chain stability.
-
Batch-to-Batch Reproducibility: In the IVD world, a slight variance in bead size can lead to failed diagnostic tests. Ask for a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) showing the CV (Coefficient of Variation).
-
Scalability of Production: Can the supplier move from 100ml to 100L without quality degradation?
-
Regulatory Support: Does the supplier provide documentation for ISO 13485 or CE-IVD compliance?
Conclusion: Future-Proofing Your Laboratory
As we move toward "Point-of-Care" (POC) testing and more sensitive liquid biopsy applications, the demand for ultra-pure silica magnetic beads is only increasing. Investing in high-quality magnetic particles today ensures that your diagnostic assays remain competitive, reliable, and scalable.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!