While Silica Magnetic Beads excel in nucleic acid purification, Magnetic Polymer Beads offer an incredibly diverse range of surface chemistries and performance characteristics, making them exceptionally versatile for a broader array of biomolecular separation and manipulation tasks. From protein purification to cell isolation and diagnostic assays, their customizable nature allows them to be engineered for precise applications where specificity, capacity, and minimal non-specific binding are paramount.

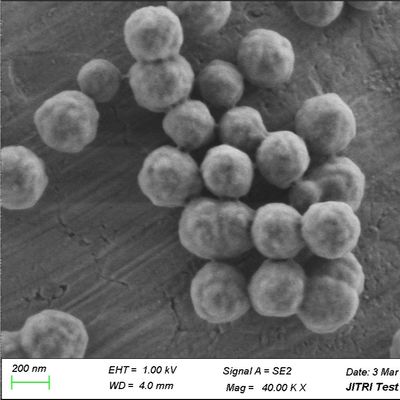
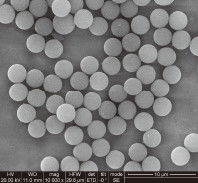
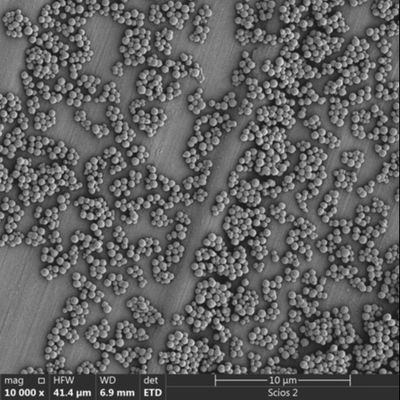
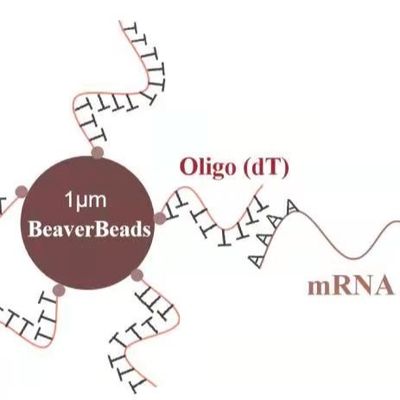
So, what are Magnetic Polymer Beads? These beads typically consist of a superparamagnetic core embedded within or coated by a polymer matrix. The polymer can be various materials, such as polystyrene, polymethacrylate, or other synthetic polymers. The key to their versatility lies in the polymer surface, which can be easily modified with a vast array of functional groups (e.g., carboxyl, amine, hydroxyl, epoxy) or pre-activated with specific ligands. This allows for a much wider range of binding chemistries compared to silica.
5μm 10 mg / mL 5 mL Magnetic Polymer Beads For Immunodiagnosis
The manufacturing process for Magnetic Polymer Beads often involves emulsion polymerization or other sophisticated techniques that allow for precise control over bead size, porosity, and surface area. This control is critical for optimizing binding capacity and kinetics.
Why are Magnetic Polymer Beads valued for their broad utility and performance?
Diverse Surface Chemistries: Unlike silica, which is primarily for nucleic acids, polymer beads can be functionalized with almost any desired chemical group. This makes them adaptable for a multitude of binding mechanisms, including:
Ion Exchange: For separating proteins based on charge.
Hydrophobic Interaction: For proteins based on hydrophobicity.
Affinity Ligands: For highly specific binding, like protein A/G for antibody purification, or antigens/antibodies for immunomagnetic separation.
Covalent Binding: For permanently attaching specific biomolecules.
High Binding Capacity: Many polymer beads are designed with porous structures or large surface areas, which significantly increases their binding capacity for target molecules, leading to higher yields in purification.
Low Non-Specific Binding: The polymer surfaces can be engineered to minimize non-specific adsorption of unwanted proteins or cellular components, leading to higher purity of the target molecule. This is crucial for sensitive assays and purification steps.
Mechanical Robustness: The polymer matrix often provides excellent mechanical stability, making the beads resilient to harsh chemical conditions, vigorous mixing, and repeated use in automated systems.
Controlled Size and Uniformity: Manufacturers can produce polymer beads with very uniform sizes, which ensures consistent magnetic response, efficient washing, and reproducibility across experiments. This is important for automated systems and high-throughput applications.
Versatility in Applications: The flexibility in surface chemistry makes Magnetic Polymer Beads suitable for numerous applications:
Protein Purification: Isolating specific proteins using affinity tags (e.g., His-tag, GST-tag), or general protein enrichment.
Immunoprecipitation (IP) / Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP): For pulling down specific proteins or protein complexes.
Cell Isolation: Separating specific cell types from heterogeneous populations (e.g., isolating immune cells from blood) by attaching antibodies to cell surface markers.
Diagnostic Assays: Used in lateral flow assays, ELISA-like assays, and molecular diagnostic kits for capturing analytes.
Enzyme Immobilization: Attaching enzymes to beads for biocatalysis or biosensor development.
In summary, Magnetic Polymer Beads are workhorses in the biomagnetic separation field. Their customizable polymer surfaces and robust design allow for precise and efficient isolation of a vast array of biomolecules and cells, making them an indispensable tool in research, diagnostics, and biotechnology where specific, high-performance separation is required.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!