Viral RNA Extraction for High-Throughput Diagnostics: The Role of Silica Magnetic Particles
SEO Keywords: Viral RNA isolation, magnetic bead RNA extraction, pathogen detection, molecular diagnostics, qPCR sample prep, viral load testing.
The Urgency of Sensitive Pathogen Detection
In the wake of global health challenges, the ability to rapidly and accurately detect viral pathogens (such as Influenza, Norovirus, or SARS-variants) has become a top priority for clinical laboratories and government agencies. The bottleneck in viral detection is often the "extraction" phase. Viral RNA is notoriously fragile and present in low concentrations. Silica magnetic beads have revolutionized this process by providing a way to concentrate viral genetic material while removing inhibitory substances.
The Science of RNA Binding to Silica
RNA extraction presents unique challenges compared to DNA. RNA is single-stranded and highly susceptible to degradation by RNase enzymes.
-
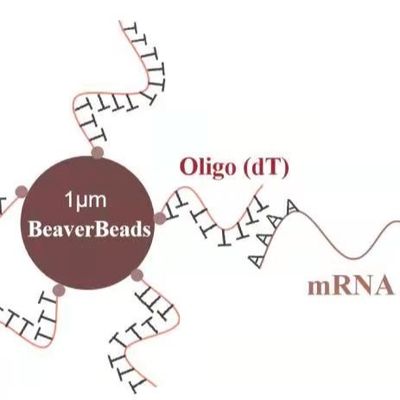
Rapid Lysis and Binding: Silica magnetic beads allow for a "one-pot" reaction where lysis and binding happen almost simultaneously. The silica surface protects the RNA from degradation by binding it tightly as soon as it is released from the viral envelope.
-
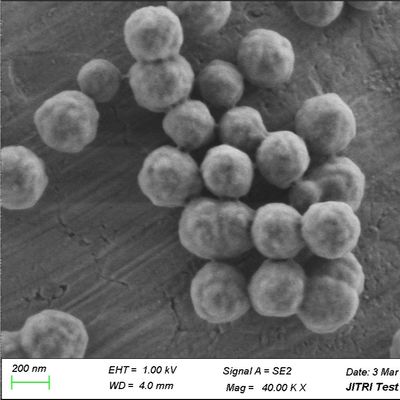
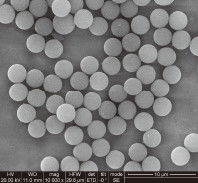
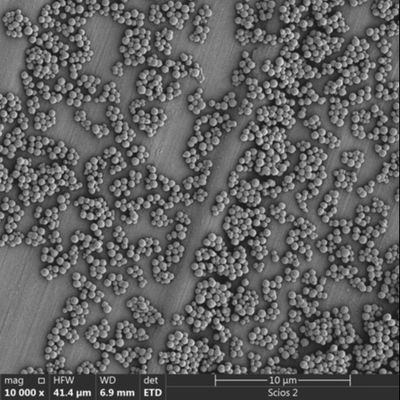
High Surface-to-Volume Ratio: Small silica beads ($<1 mu m$) provide an enormous surface area, which is crucial for capturing the tiny amounts of RNA found in viral transport media (VTM).
Engineering for Low "Limit of Detection" (LoD)
For a diagnostic kit to be successful, it must be able to detect the virus even at very low viral loads. Engineers optimize silica beads for this by:
-
Minimizing Background Noise: High-purity silica ensures that no "junk" DNA or protein is co-purified, which could interfere with the fluorescent signals in qPCR.
-
Efficient Elution: The beads are designed to release nearly 100% of the bound RNA in a very small volume (e.g., $20 mu L$), effectively "concentrating" the sample by 10x or 20x.
-
Optimizing Porosity: While non-porous beads are easier to clean, slightly porous silica beads can offer higher binding capacity for small viral fragments.
Procurement Strategy: Security of Supply for Pandemic Preparedness
From a procurement standpoint, viral RNA extraction beads are considered "strategic assets."
-
Stockpiling and Stability: Procurement officers must source beads that have a documented shelf-life of at least two years at room temperature. This is essential for maintaining "surge capacity" in case of a sudden outbreak.
-
Global Logistics: Choosing a supplier with decentralized manufacturing prevents supply chain disruptions caused by regional logistics failures.
-
Compatibility with Universal Lysis Buffers: It is beneficial to procure silica beads that are "buffer-agnostic," meaning they work well with various proprietary lysis recipes from different kit providers.
High-Throughput Automation in Clinical Labs
Modern clinical labs process thousands of samples a day. Silica magnetic beads facilitate this through:
-
Short Magnetic Separation Times: High-emu cores allow for separation in under 30 seconds.
-
Compatibility with "Deep Well" Plates: Ensuring the beads don't stick to the plastic walls of the 96-well plates.
-
Reduced Manual Intervention: Minimizing the risk of cross-contamination between patient samples.
Conclusion: The Future of Viral Surveillance
As we look toward 2026, the integration of silica magnetic beads into "Point-of-Care" and "Near-Patient" testing will continue to grow. By providing a reliable, fast, and scalable way to isolate viral RNA, these microscopic particles remain at the frontline of global infectious disease management.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!