In the fast-paced world of life sciences, from diagnostic development to drug discovery and basic research, the ability to efficiently separate and purify specific biomolecules is absolutely crucial. Traditional methods often involve cumbersome and time-consuming steps like centrifugation or chromatography. This is where Magnetic Beads step in as a transformative technology, revolutionizing biomolecular separations by offering a simple, rapid, and highly effective alternative.
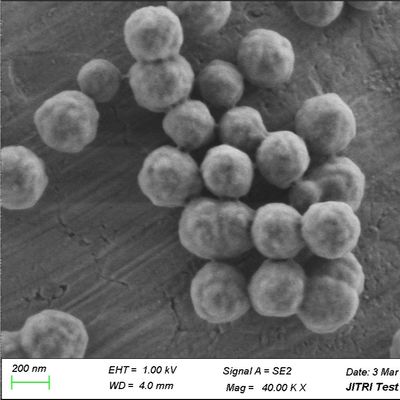
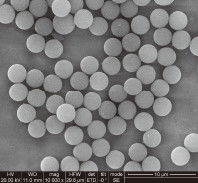
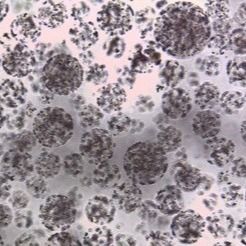
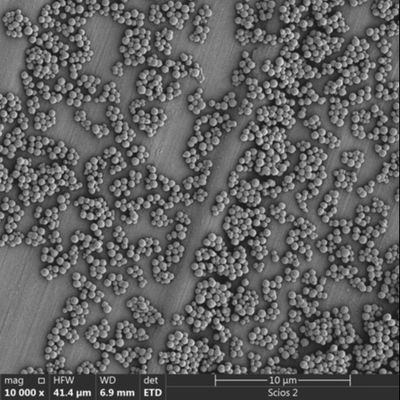
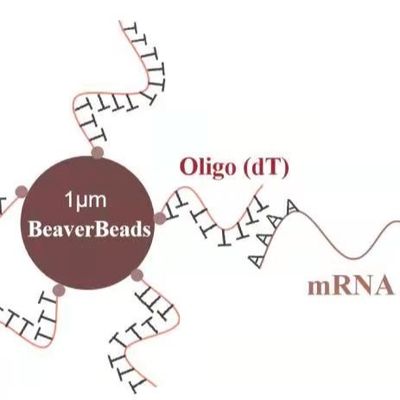
So, what exactly are Magnetic Beads? At their core, they are microscopic spheres (ranging from nanometers to micrometers in diameter) that contain magnetic material within their core. This magnetic core allows them to be easily manipulated by an external magnetic field. The true power of magnetic beads, however, lies not just in their magnetism, but in their surface chemistry. Their surfaces are engineered to be functionalized, meaning they can be coated or derivatized with various chemical groups or biomolecules that specifically bind to target substances.
The process of using magnetic beads for biomolecular separation is remarkably straightforward:
Binding: Magnetic beads, functionalized with a specific ligand (e.g., an antibody, an oligo, or streptavidin), are added to a sample containing the target biomolecule. The ligand on the bead surface selectively binds to the target.
Washing: An external magnet (often a simple magnetic rack) is applied to the side of the tube or well. This draws the magnetic beads, along with their bound targets, to the wall of the container, forming a pellet. The supernatant, containing unbound impurities, can then be easily aspirated and discarded. This step is repeated with wash buffers to remove any remaining non-specifically bound molecules.
Elution (Release): Once the beads and targets are thoroughly washed, the magnet is removed. A specific elution buffer is added that disrupts the binding between the beads and the target, releasing the purified biomolecule into the solution. The magnet is then reapplied to separate the beads from the now-purified target.
The simplicity and power of this "bind, wash, elute" process offer numerous advantages over conventional separation techniques:
Speed and Efficiency: Magnetic separations are incredibly fast, often taking minutes instead of hours, greatly accelerating workflows.
Ease of Automation: The magnetic separation process is highly amenable to automation, allowing for high-throughput processing in multi-well plate formats, which is essential for large-scale research and diagnostic testing.
Reduced Sample Loss: The gentle nature of magnetic separation minimizes sample loss often associated with centrifugation or filtration, which can be critical for precious or limited samples.
No Contamination: Being a "closed system" during separation, the risk of cross-contamination is significantly reduced.
Versatility: Magnetic beads come in various sizes, surface chemistries, and core materials, making them adaptable for isolating a wide range of biomolecules, including DNA, RNA, proteins, cells, and even viruses.
From isolating nucleic acids for PCR, purifying antibodies for diagnostics, enriching specific cells for therapeutic applications, to developing novel biosensors, Magnetic Beads have truly revolutionized biomolecular separations. They provide a powerful, user-friendly, and highly efficient tool that is essential for advancing research, diagnostics, and therapeutic development in modern laboratories worldwide.
Blood DNA Kit For Blood DNA Extraction For Automatic Operation

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!